Acceleration
Signiant has long been a market leader in advanced transport technology, holding several patents in this area, and our software is relied upon to move petabytes of high-value content every day.
Each of Signiant’s products leverages our proprietary acceleration technology, moving content up to 100x faster than standard Internet transmission speeds. Signiant’s acceleration technology is capable of moving any size file or data set over any IP network, while taking advantage of all available bandwidth.
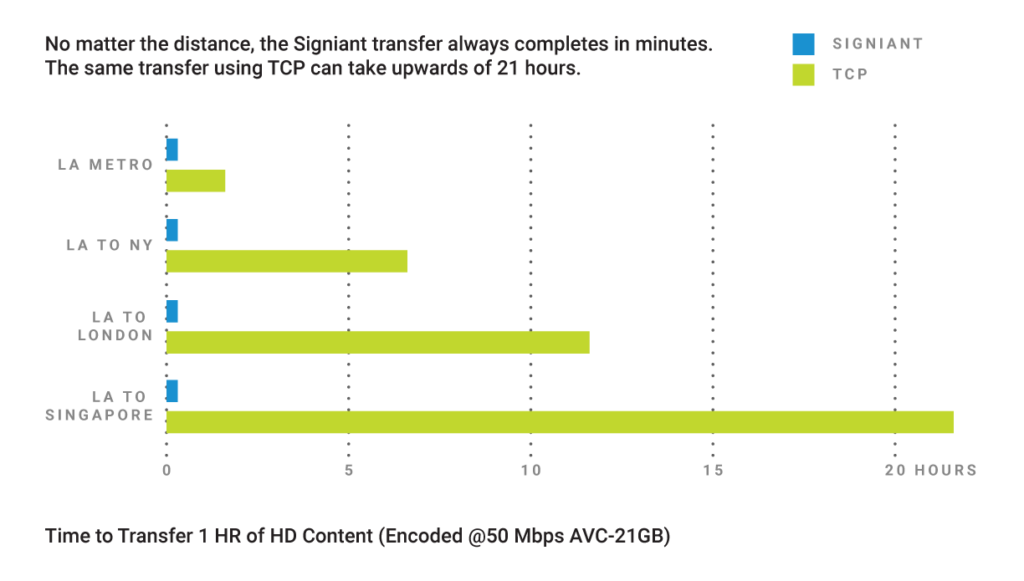
While our transport technology adds value in many situations, the speed difference is most notable with large data sets, long distances or highly-congested networks and, somewhat counter-intuitively, when there is more bandwidth.
- Signiant’s transport technology eliminates the impact of latency and packet loss
- The entire file is always sent byte for byte, without compression
- Signiant adds Checkpoint Restart on top of its transport technology to automatically restart any interrupted transfer from the point of failure, without losing data
Signiant UDP
Signiant’s patented acceleration technology is often casually (and somewhat incorrectly) referred to as “UDP acceleration“, and it does run over UDP. But Signiant’s innovation goes far beyond that passing resemblance to deliver high speed over UDP with TCP-like reliability. To make UDP more dependable, Signiant implements TCP functionality in a far more performant way by optimizing:
- Flow control – makes sure data is transmitted at the optimal rate for the receiver
- Congestion control – detects when the network is being overloaded and adapts accordingly
- Reliability mechanisms – ensures that data loss due to congestion or other network factors is compensated for and that the order of the stream of data is maintained
Using constant measurements of effective throughput, network latency and packet loss, Signiant’s technology catalogues and analyzes the frequency of changes to locate points of network congestion. This approach affords far more efficiency than congestion control algorithms that react to simple point-in-time packet loss.

PostOffice Films
Dávid Jancsó, Film Editor
“It [Media Shuttle] saves us tons of time and helps us to properly communicate with our editors around the globe.”
Learn More About the Signiant Platform
The Signiant Platform builds on the foundation of our world-class fast file movement apps and adds workflow-centric production services that make working with media even more efficient.
Thank you for your interest in Signiant!
A product specialist will reach out to you shortly.
Signiant's Next-Generation Intelligent Transport
Signiant’s patented intelligent transport (currently available in Jet and Flight Deck) leverages the power of machine learning to analyze anonymized historical data, plus the current network conditions and available compute resources, to select the best combination of transfer settings at a given moment. Every time the SDCX SaaS architecture accesses a media asset, information about the settings used, the operating environment, and the results achieved is collected by our SaaS service and used to inform future transfer decisions.
Signiant’s intelligent transport eliminates the need for time-consuming, error-prone manual configuration by evaluating network conditions, computing resources and storage types to identify the best choices for three primary settings: the transfer protocol, the number of parallel streams, and the use of pipelining. After analyzing a wide variety of inputs, the intelligent transport may choose to use Signiant UDP or standard TCP, and will determine the optimal number of parallel streams along with other settings to automatically adapt and optimize performance on any IP network.
Signiant’s fastest transport yet is capable of multiple Gbps speeds!
Read more about Signiant’s Intelligent Transport in our Metadata Everywhere series.
